
Autonomous Wildfire Surveying Drone
2025, May 30
Overview
This project, developed as a capstone at the University of Toronto, addresses the urgent need for improved situational awareness during wildfires. Our solution is an autonomous quadcopter that detects wildfire hotspots and human survivors, then maps these findings in real time to assist emergency responders.
Using onboard perception and mapping, the system identifies hazards, geolocates them, and builds a 2D occupancy grid to guide search-and-rescue operations.
Building and Configuration
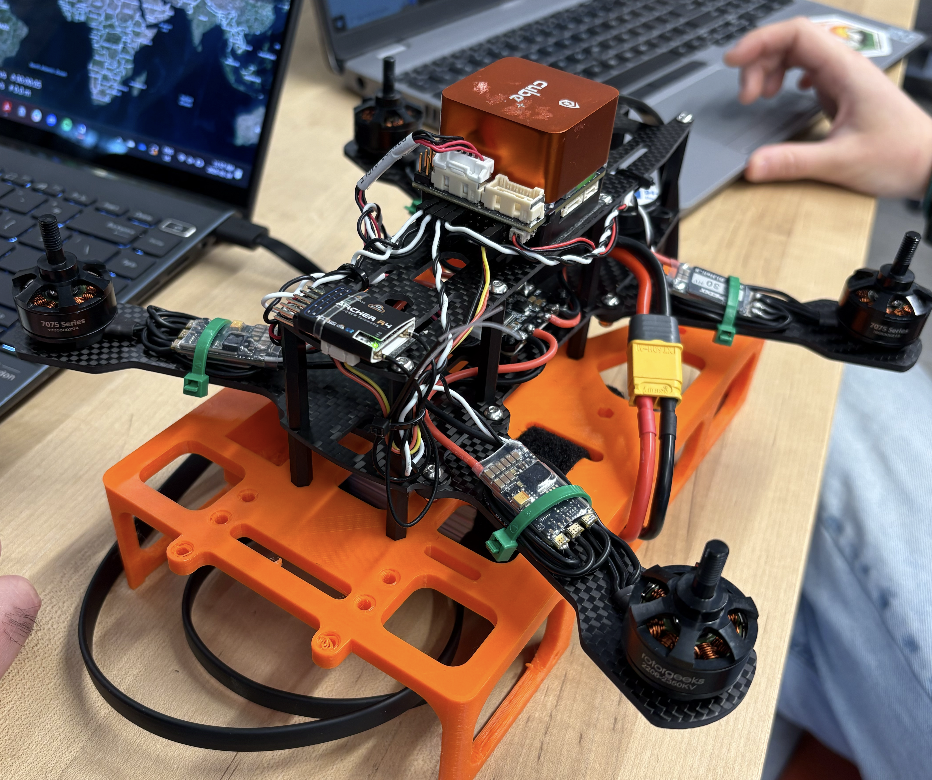
- Hardware:
- Frame: Lightweight carbon fiber frame with four motors and ESCs.
- Flight Controller: CubePilot Orange Cube+ with PX4 autopilot firmware.
- Motors & ESCs: Four brushless motors connected to ESCs.
- Remote Control: Taranis Transmitter and Archer R4 receiver.
- Sensors: TeraRanger EVO for distance measurements, integrated buzzer.
- Software: PX4 firmware on the Cube+ and QGroundControl for setup and monitoring.
- Onboard Computer: Jetson Nano for future image processing and autonomy.
- Camera: Sony IMX219 RGB camera for human detection and Intel RealSense T265 for visual-inertial odometry.
- Software: ROS2 Foxy on Ubuntu 20.04 for perception, mapping, and planning.
Calibration of camera and grid setup
- Propeller Direction: Properly configured the propellers by ensuring the correct clockwise (CW) and counterclockwise (CCW) orientation of the motors. This step ensures stable flight by matching motor rotation with the correct propeller direction.
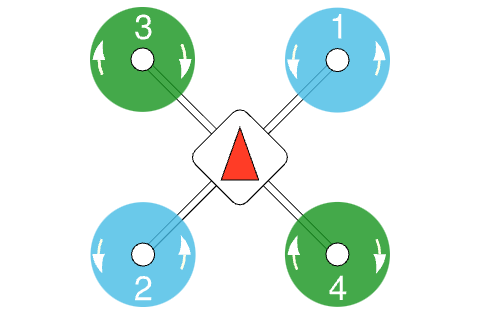
System Architecture
- Perception:
- Intel RealSense T265 for visual-inertial odometry.
- Sony IMX219 RGB camera with SSD-Mobilenet-v2 for human detection.
- ArUco marker detection to simulate fire signatures.

- Projection:
- Bounding boxes and ArUco marker centroids are back-projected from image space into the ground plane using camera intrinsics and the drone’s real-time pose from the Intel RealSense T265.
- Mapping:
- Real-time occupancy grid fusing detections and pose data, published as ROS2
nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid. - Log-odds 2D occupancy grid continuously updates, fusing projected detections with pose data.
- Real-time occupancy grid fusing detections and pose data, published as ROS2
- Visualization:
- Green markers: fire detections .
- Red markers: human detections (candidate rescue targets).
- Grey cells: confirmed human presence.
- Black cells: confirmed fire location.
- Outcome:
- Produces live situational awareness, showing firefighters where hazards and survivors are located in the surveyed area.
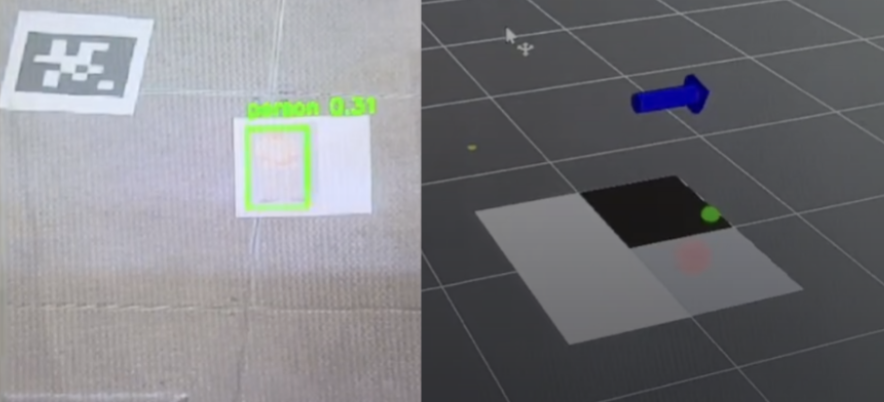
Example of real-time occupancy grid mapping with fire (black) and human (grey) classifications. (red ball = real time human detection, green box = real time fire (ArUco) detection)
- Planning & Navigation:
- Phase 1: Structured “lawnmower” sweep of the environment.
- Phase 2: Revisits detected humans by lowering altitude for closer inspection.
- Onboard Compute: NVIDIA Jetson Nano running ROS2 for perception, mapping, and planning.
- Flight Control: Cube Orange with PX4 firmware for stabilization and waypoint following.
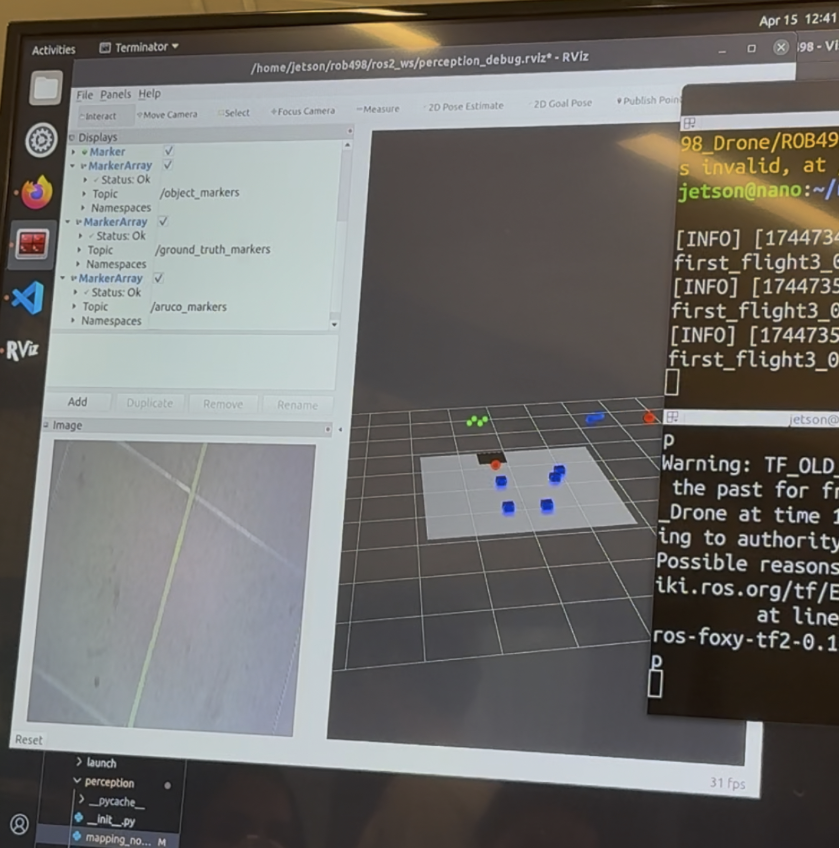
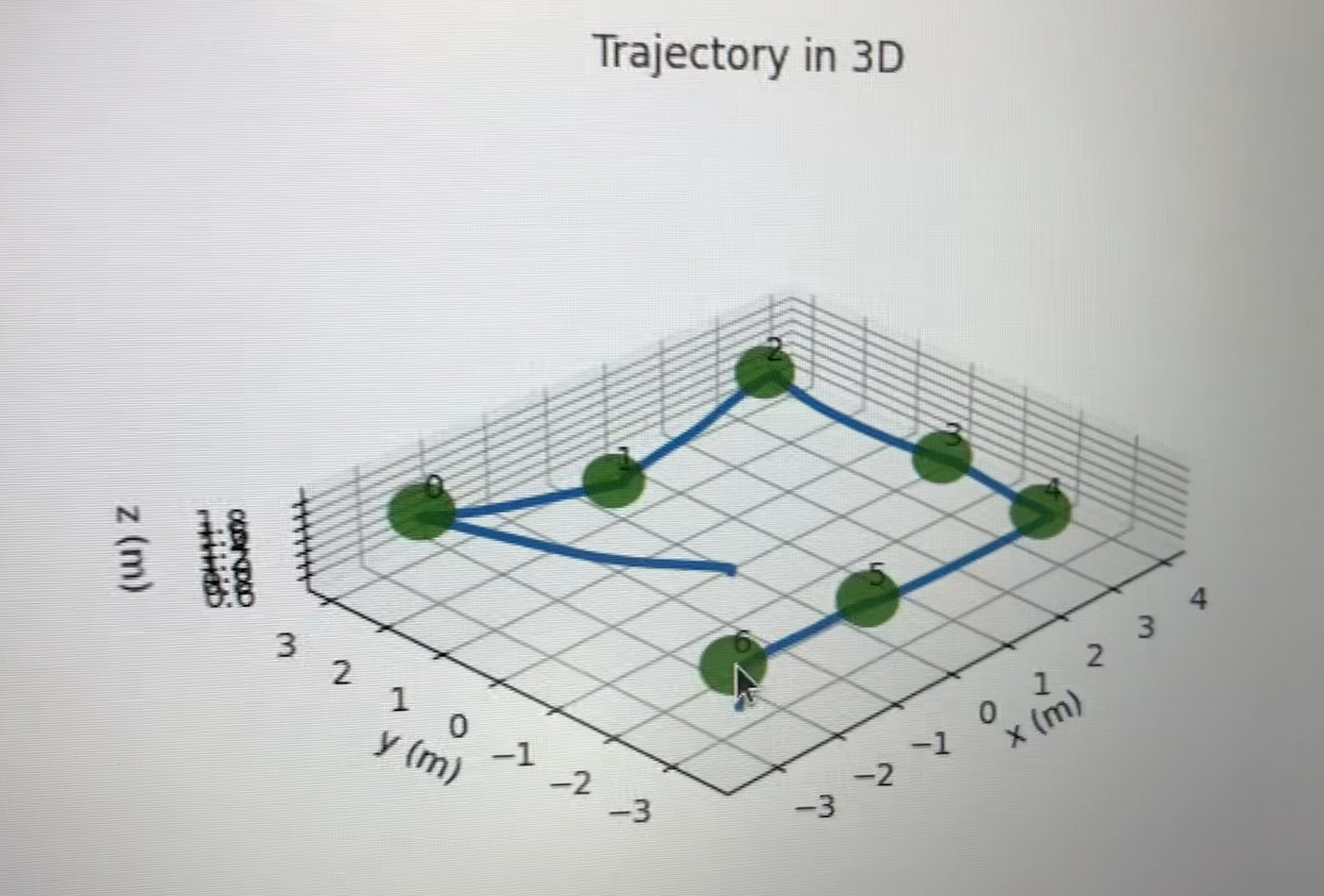
- Autonomous Flight:
- preplanned waypoint for area coverage
- final position map outlines drone flight path and waypoint coverage (green dots)
Results
- Achieved autonomous area coverage using a lawnmower pattern.
- Real-time detection and geolocation of simulated fire and human markers.
- Successful fusion of detections into a live occupancy grid.
- Demonstrated robust system integration of perception, mapping, and planning entirely onboard the drone.
Future Work
- Integrating thermal cameras and LiDAR for real-world deployment.
- Expanding from 2D to 3D mapping for varied terrain.
- Scaling compute power (e.g., Jetson Orin) for higher-throughput models like YOLO-v8.