Autonomous Mini-Car with IR and Ultrasonic Navigation
Overview
Developed an autonomous mini-car capable of line-following and obstacle avoidance using infrared (IR) and ultrasonic sensors. The car employs a “Fancy Bang-Bang” control algorithm for smooth navigation, overcoming motor limitations for precise control.
Watch the Demo
Key Features
- Line Following: Utilized IR sensors to detect the track and applied the “Fancy Bang-Bang” algorithm to adjust motor speeds for smooth turns and transitions.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Incorporated ultrasonic sensors with a servo motor to detect objects in the path and autonomously navigate around them.
- C++ Implementation: Wrote modular, efficient C++ code to integrate both the line-following and obstacle-avoidance features seamlessly.
How It Works
- Sensor Integration: The IR sensors track the line on the ground, while the ultrasonic sensor detects obstacles ahead, providing a real-time “point cloud” for navigation.
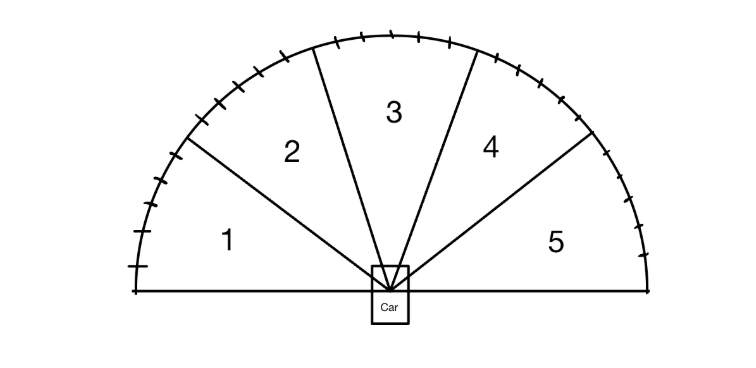
- Control Algorithm: The “Fancy Bang-Bang” algorithm adjusts motor speeds based on sensor inputs, allowing the car to navigate tight turns while avoiding obstacles.
- Testing & Optimization: Conducted thorough testing to minimize motor oscillations and fine-tune the system for real-world performance.
Technical Overview
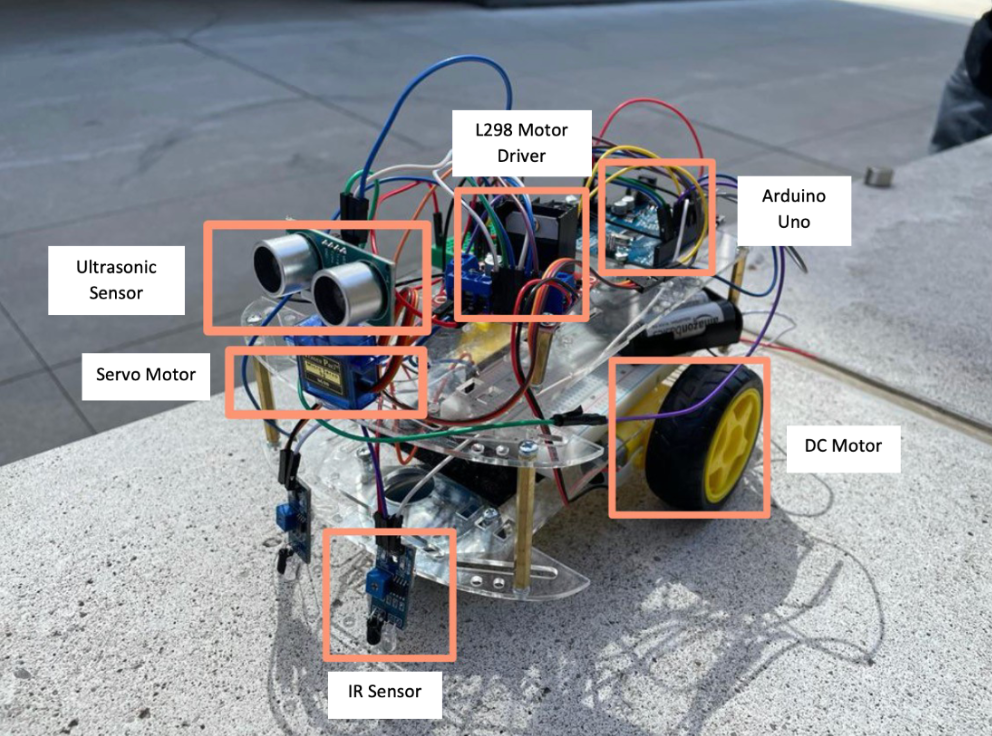
-
Sensor Polling:
The system continuously polls the IR and ultrasonic sensors, collecting measurements for line checkpoints and object distance. -
Control Input Computation:
Based on the current and historical measurements from the IR sensors, the system computes the control input needed for accurate line-following. -
Object Detection and Avoidance:
Using distance measurements from the ultrasonic sensor, the system determines if an object is detected and initiates object avoidance routines if necessary. -
Surroundings Scan:
The system scans its surroundings by gathering 20+ floating-point measurements. The exact number depends on the required precision for the environment. -
Steering Decision:
By analyzing the difference between the two IR sensor readings, the system decides whether to steer right or left to stay on track. -
Motor and Servo Control:
Control inputs are then sent to the servo and motors to adjust the vehicle’s movement according to the computed decisions.
Technologies Used
- C++
- Arduino IDE
- IR Sensors
- Ultrasonic Sensors
- Servo Motors
Results
Successfully built and demonstrated an autonomous mini-car that can follow paths and avoid obstacles in real-time. This project showcases skills in embedded systems, sensor fusion, and efficient algorithm design.
Look at the Code!
github link: Big Bang Racer Code
